
You can see two sets of parallel lines which are your focus indicators.

Reduced size below can be downloaded (as a Zipped JPEG) HERE I've written this article so that users can test their DSLR under a set of Result of either a camera or a lens calibration problem. Note also that both the camera and lens are involving in focusing. If it doesn't look sharp, focus is not likely to be in spec. So the bottom line is that focus should be within the DOF, or to put it another way, With slowerīodies reverts to the same as that of "consumer" bodies which don't have the On the "pro" bodies (EOS 1 series) focus spec for f2.8 and faster lenses (f4 on some models) is that it should be within 1/3 of the DOF. It should be within the DOF (Depth of Field). "consumer" bodies (such as the Digital Rebels and the EOS 20D/30D/40D) is that For example, Canon state that the spec for focus on Of course no manufacturer of cameras or lenses claims that autofocus isĪbsolutely perfect. May be due to technical problems with AF, but some are due to user error or unreasonable user expectations. Sometimes the focus point is in front of the intended subject and sometimes it's behind it. The line pair (lp) means a black and a white line.Part 5 - Focus Accuracy Check (for AF lenses)Ī common complaint seen on web photo forums is that cameras (and/or lenses) aren't achieving accurateįocus. Resolution (lp/mm) = 2 Group + ( element − 1 ) / 6 Īlthough usually the following lookup table will be more convenient to use. The scales and dimensions of the bars are given by the expression
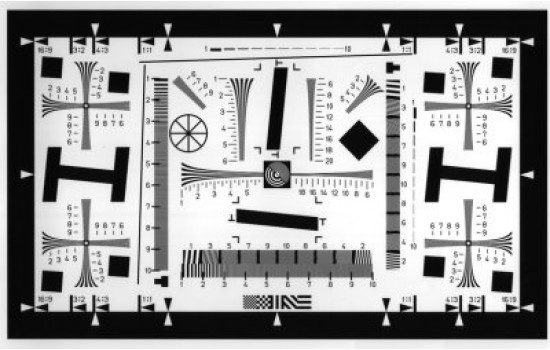
The first element of the even-numbered groups is at the lower right of the layer, with the remaining 2 through 6, at the left. Within the same layer, the odd-numbered groups appear contiguously from 1 through 6 from the upper right corner. Each group consists of six elements, numbered from 1 to 6. The smaller layers consist of repeating progressively smaller pairs toward the center. The largest two groups, forming the first layer, are located on the outer sides. The common MIL-STD-150A format consists of six groups in a compact spiral arrangement of three layers.
Optical aberrations in the imaging system are readily detected and characterized by translating and rotating the elements within the imaging system's field of view.
#Fokus test chart series
This pair of digits indicates a given element's row and column location in the series table, which in turn defines the spatial frequency of each element, and thus the available resolution of the system.Īn analytical characterization of resolution as the modulation transfer function is available by plotting the observed image contrast as a function of the various element spatial frequencies. This element's label is noted by the observer (each group, and each element within a group, is labeled with a single digit). The largest element observed without distinct image contrast indicates the approximate resolution limit. In practice, the spatial resolution of an imaging system is measured by simply inspecting the system's image of the slide. A less expensive, abbreviated version omits the two tiniest groups at the center of the pattern (Group Number 8 and 9), since the lithography at that scale is costly, and the group elements represent resolution beyond the design of many imaging applications. Slides are available as photographic positive or negative prints to best fit the illumination technique used in various testing methods. The slide is printed in metallic chromium via photolithography with the standard pattern, photographically reduced from a large master plot. The series of elements spans the range of resolution of the unaided eye, down to the diffraction limits of conventional light microscopy.Ĭommercially produced devices typically consist of a transparent square glass slide, 2 inches or 50mm in dimension. These 54 elements are provided in a standardized series of logarithmic steps in the spatial frequency range from 0.250 to 912.3 line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm). Each element consists of three bars which form a minimal Ronchi ruling.
#Fokus test chart full
The full standard pattern consists of 9 groups, with each group consisting of 6 elements thus there are 54 target elements provided in the full series. It is widely used in optical engineering laboratory work to analyze and validate imaging systems such as microscopes, cameras and image scanners. The design provides numerous small target shapes exhibiting a stepped assortment of precise spatial frequency specimens. A 1951 USAF resolution test chart is a microscopic optical resolution test device originally defined by the U.S.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
